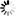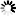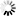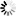|
What is a Power Supply?
In general, a source of power
is a source of energy, this energy can be of various types, thermal, nuclear,
electric, etc. In the middle of electronics, most people call power source to
an electrical circuit which converts the electricity from AC voltage (Vac Vac
or English) to a DC voltage (Vdc Vdc or English).
The AC voltage or Vac is, for
example, we get from the outlet of our homes, the voltage and current is
alternating as its polarity varies with a specific frequency. For example,
Mexico nominal voltage is 110 volts at 60 Hz. The same used in USA, but
different than it has for example in Argentina, Japan and Europe.
The direct voltage has a
fixed frequency unchanged polarity. This voltage is used by the vast majority
of electronic circuits, example of this voltage is found in alkaline batteries
or rechargeable type found for example in the mobile phone.
Most electronic circuits used
direct voltage, but always have a type of power source that converts Vac to
Vdc, the source can be external or internal. A battery charger is considered a
source of power, which transforms the Vac to Vdc to charge the rechargeable
battery.

The illustration shows a typical charger that converts input Vac
to Vdc which has an input is shown 110-240 volt s AC with frequency
of 50-60 Hz and demand 0.2A at the entrance. The output is a voltage
CD of 5 volts with 0.8 to 1 ampere output. The maximum output power
is 5 watts.
The AC voltage is used to
transmit electricity from one point to another, the more distant it is a point
on the other, the greater the energy loss by transmission to minimize this
loss, the voltage is increased to several thousand volts with small streams
using transformers rise. Down transformers are used when electricity is
approaching its final destination.
Power supplies can be very simple
or very complex, the simplest type is the black box we put into the socket to
charge your mobile phone. The specifications of these sources are the output
voltage specified in volts and current capacity, specified in amperes or power,
which is the result of multiplying the voltage and the maximum current
available. Power is expressed in watts.
Computers bench power supplies
use high efficiency providing several fixed voltages via standard connectors,
these sources provide fixed voltages of +5, +12 and -12 volts through several
identical connectors that connect to the main board, hard drives and other
computer components.
People who design postcards, engineering
students and researchers often use power sources to power their circuits or
experiments. These sources are usually variable output, you can vary the level
of voltage and current manually with separate knobs. Such sources typically has
voltage and current indicators. The voltage is varied so that the circuits
operate correctly, the current that is supplied is limited to prevent damage to
the components during the assembly under test this evil assembly or designed. The figure shows a DC power
supply with variable output. The digital display shows isolate from electrical supply
voltage or output. You can work in CC mode (constant current) or CV (constant voltage),
an LED indicates the mode in which it operates. There knobs dedicated to
adjusting fine or coarse voltage or current voltage. Three terminals have. One
for the positive voltage (red) One for the negative (black) and earth ground (Green). CC mode or constant current can
be used in chemical processes that require the passage of a current for a
period of time to create a reaction.
The electronic designer may have
analog and digital electronics in your circuit, and this designer requires a source
that can provide more than one voltage source simultaneously. A source for
powering digital logic circuits, and two other sources that feed the analog
circuitry with two voltages of opposite polarity. A common source of power in
an electronics laboratory has a set of three outputs, about 5V and two other
variables with ranges of 0-30 volts.
Typical Lab Power Supply. They are used in schools and research centers power electronic circuits under test.
This model provides 3 independent outputs with ranges of 0-30 and 0-3 volts amperes and a fixed output of
5 volts with a current of 0-3 A. These sources are very flexible because the variable outputs can be configured
in serial mode or parallel to obtain twice the voltage or current output.
The outputs of power supply are
usually floated. This reference to the negative voltage circuit, which might be
different from the physical land of the electrical installation. Another reason
that the outputs of the sources are floated is to reverse the polarity, or to
connect them serially or in parallel to double the capacity of voltage in the
first case or the current capacity in the second case.
The sources laboratory for
testing prototypes are low power, with a range of 80-300 watts, with one to
four individual outputs for added flexibility.
For applications that require
more power and broader voltage and current ranges have high power sources,
there are output from 600W up to several tens of kilowatts. Applications for
these sources can be found in itself is manufactured, which is required to feed
multiple circuits simultaneously, or simulate high current batteries like those
found in cars or airplanes. Sometimes these high power sources are used for
chemical process like chrome or ionization. The sources of high power and high
efficiency for the use of processes from manufacture is designed to be
rack-mounted, as they are part of an instrument panel. This source has control
of voltage and current type of lock that prevents the parameters are moved by
someone outside the process or by mistake. This source has up to 3 KW or KVA
output.
The control of sources can be
done manually by varying the voltage and current knobs. But in a plant from
manufacture, for example, requires that a controller or computer to communicate
with the power to control it remotely. There are several ways to remotely
control a source of power, including remote control options can mention RS232,
GPIB, USB and Ethernet LAN port. There are some similar methods that control
the output using a signal proportional to the desired voltage output analog
control and a signal for switching on or off of the exit.
An application where the remote
control is used using a computer is in a factory breakers where they check each
of the breakers applying the necessary current to cause the breaker it acts off
the power, an automatic system can increase the current to some extent and
sensing that current the breaker acts, a signal controller can send the breaker
a lot of good breakers or separate it defective.  Above the rear of the power source
in the above mentioned figure shows. From left to right and top to bottom we
can see first terminals of the output DC (direct current). In the sources of
high output power is requires a professional electrical installation where
three phases indicated here as L1 / F1 are used, L2 / F2 and L3 / F3, each
phase with its own fuse. Bottom right is the D type connector for remote
control, useful for controlling the source with a PLC. The two cables whites
who go to a J11 connector on the bottom. This is the connection sensing that
helps to compensate for the voltage drop in output cables, by default connect
directly departure, but can be connected to the load to compensate voltage
drops. Power supplies laboratory usually
also have terminals sensing , in English called sense , a positive terminal and
a negative , these terminals are used to compensate for voltage drop that
occurs in the cables from the power supply to the assembly under test.
There are also sources of AC
power, the input of these sources is also AC voltage The difference is that a
laboratory source AC can vary its output voltage very accurately, vary its
frequency, and in some cases even vary the harmonic content to stress font
designs that transform VAC to VCD or test voltage -operated machines alternate,
as AC motors, which use one or more stages.
Classification of Power Supplies.
Figure 1: Power Supply
Also known as Power
Supply can be defined as circuits that
transform the input power , and either AC or DC ; in output AC or DC .
This definition excludes Energy source based on the principle of a rotating machine and
distinguishes the Power Supply most
of the Energy sources that get their
power from other forms of energy.
There are four general classifications for Power Supply:
1. Input AC - AC Output: Line Regulators and frequency
changers
2. Input DC - DC Output: DC Converters & Regulators
3. Input DC - Output AC: Inverters
4. AC Input - Output DC
The last category is the most common of all and which is
usually referred to as Power Supply.
There are also four modes of operation that the power
supply may provide DC output: · Constant output voltage: The output voltage
remains constant despite changes in load, temperature or line. A DC power
source would ideally zero output impedance at all frequencies. For a constant
output without curling effect a control element or control technology is
required Regulatory technical best known are :
a) Linear Regulation
b) Pre series regulation or
regulation
c) Switched
d) Through SCR
·
Constant current output: The output current
remains constant despite changes in load , output, or temperature. The power
source that provides constant current should have an infinite impedance at full
output frequency. This type of power supplies constant current has many
applications in circuit design and semiconductor test.
·
Limit voltage
·
Current limit
The power source may be
programmable by means of a computer with USB communication ports, Ethernet (LXI
) , GPIB or RS232. These interfaces are used in automated test and measurement
systems.
Some power supplies can be
programmed from the front panel with a specific routine work, such as SGI
series of Sorensen.
The power output of a source is
obtained by multiplying the maximum voltage and current capacity. Thus, a
source that generates an output voltage of 300 volts DC at 10 amperes have a
capacity of (300 x 10 ) 3000 Watts or 3 KW ( Kilo - Watts ).
Consideraciones y
Especificaciones a Considerar en Fuentes de Poder. ·
Noise and Ripple Output
It refers to RMS
or peak to peak voltage variation that has the output power source.
·
Transient Response
It is the supply capacity to meet
current demands great variation in short periods of time
·
Speed up or down (slew-rate)
Is the speed with which the power
source is turned on, off or varies the voltage or output current from an
instruction for a communication port or via manual controls.
·
Load Regulation
Sets Supply
Ability to maintain a constant voltage when the load varies.
·
Line Regulation
The AC power line may vary from
one country to another, or simply a place to another, the power supplies must
be able to regulate their output even when the AC input voltage has a variation
within specification working source.
·
Stability
Stability is specified as the
ability to maintain the output voltage and current over a long period of time.
·
Efficiency
The percentage of conversion
efficiency of the input power from the power source output.
|
|
|